추천시스템 튜토리얼
본 게시물은 추천시스템에 대한 구현으로 해당 포스트를 읽고 정리하는 글이다.
1. Introduction
추천 시스템의 목적은 사용자의 선호도를 바탕으로 관련된(relevant) 아이템을 추천해주는 것이다. 이때의 선호도와 관련도는 주관적이며, 일반적으로 사용자가 이전에 소비했던 아이템들을 바탕으로 추론한다.
추천 시스템의 주요 기법들은 다음과 같다.
-
Collaborative Filtering
여러 사용자들의 선호도 또는 취향을 수집하여(collaborating) 사용자의 관심사에 대한 예측(filtering)을 수행한다.
협업 필터링 접근법의 기본적인 가정은 어떤 아이템 집합에 대해 A가 B와 같은 의견을 가지고 있다면, 임의로 주어진 아이템에 대해 A는 다른 사용자보다 B와 유사한 의견을 가진다는 것이다. -
Content-Based Filtering
사용자가 이전에 소비한 아이템의 설명과 속성에 대한 정보만을 사용하여 사용자 선호도를 모델링한다.
즉, 이 알고리즘은 이전 사용자가 과거 선호했던 아이템을 추천한다.
특히 사용자에 의해 평가된 이전 아이템들과 다양한 후보 아이템들을 비교하고, 가장 잘 맞는 아이템을 추천한다. -
Hybrid Methods
collaborative filtering과 content-based filtering을 결합한 hybrid approach은 개별 모델보다 효과적이다.
추천 시스템의 cold start 및 희소성 문제 등을 해결하는데 사용 될 수 있다.
현재의 연구 동향은 딥러닝을 활용한 기법들이며 성능 또한 기존의 방법들에 비해 향상됨을 증명하였다. 이에 대한건 다른 포스트에서 다룰 예정이며 이곳에서는 캐글 데이터셋을 통해 위 기법들에 대한 실습을 진행한다.
2. Data
import numpy as np
import scipy
import pandas as pd
import math
import random
import sklearn
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
from scipy.sparse.linalg import svds
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
-
shared_articles.csv
이 데이터는 플랫폼에 기재된 기사들이며, 각 기사에는 날짜(timestamp), 원본 URL, 제목, 일반 텍스트의 내용, 기사의 언어(포르투갈어: pt 또는 영어: en) 및 기사를 등록한 사용자(작성자)에 대한 정보가 있다. timestamp는 아래 두 가지 이벤트 유형을 가지고 있다. 정확한 시나리오는 주어진 시간에 사용할 수 있는 기사만 추천을 하는 것이지만, 이번 실습에서는 단순성을 위해 “CONTENT SHARED” 이벤트 유형만 고려한다.
- CONTENT SHARED: 플랫폼에 공유됨
- CONTENT REMOVED: 플랫폼에서 제거됨
articles_df = pd.read_csv('./data/shared_articles.csv').loc[lambda d: d['eventType'] == 'CONTENT SHARED']
articles_df.head()
| timestamp | eventType | contentId | authorPersonId | authorSessionId | authorUserAgent | authorRegion | authorCountry | contentType | url | title | text | lang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1459193988 | CONTENT SHARED | -4110354420726924665 | 4340306774493623681 | 8940341205206233829 | NaN | NaN | NaN | HTML | http://www.nytimes.com/2016/03/28/business/dea... | Ethereum, a Virtual Currency, Enables Transact... | All of this work is still very early. The firs... | en |
| 2 | 1459194146 | CONTENT SHARED | -7292285110016212249 | 4340306774493623681 | 8940341205206233829 | NaN | NaN | NaN | HTML | http://cointelegraph.com/news/bitcoin-future-w... | Bitcoin Future: When GBPcoin of Branson Wins O... | The alarm clock wakes me at 8:00 with stream o... | en |
| 3 | 1459194474 | CONTENT SHARED | -6151852268067518688 | 3891637997717104548 | -1457532940883382585 | NaN | NaN | NaN | HTML | https://cloudplatform.googleblog.com/2016/03/G... | Google Data Center 360° Tour | We're excited to share the Google Data Center ... | en |
| 4 | 1459194497 | CONTENT SHARED | 2448026894306402386 | 4340306774493623681 | 8940341205206233829 | NaN | NaN | NaN | HTML | https://bitcoinmagazine.com/articles/ibm-wants... | IBM Wants to "Evolve the Internet" With Blockc... | The Aite Group projects the blockchain market ... | en |
| 5 | 1459194522 | CONTENT SHARED | -2826566343807132236 | 4340306774493623681 | 8940341205206233829 | NaN | NaN | NaN | HTML | http://www.coindesk.com/ieee-blockchain-oxford... | IEEE to Talk Blockchain at Cloud Computing Oxf... | One of the largest and oldest organizations fo... | en |
-
users_interactions.csv
기사에 대한 사용자 상호작용 로그이며, contentId 컬럼을 통해 articles_shared 데이터와 조인할 수 있다. 상호 작용에 대한 유형(eventType)은 아래와 같다.
- VIEW: 사용자가 문서를 열었습니다.
- LIKE: 사용자는 그 기사를 좋아했습니다.
- COMMENT CREATED: 사용자가 기사에 주석을 작성했습니다.
- FOLLOW: 사용자는 기사의 새로운 댓글에 대해 알림을 받기로 선택했습니다.
- BOOKMARK: 나중에 쉽게 반환할 수 있도록 사용자가 문서에 책갈피를 추가했습니다.
interactions_df = pd.read_csv('./data/users_interactions.csv')
interactions_df.head()
| timestamp | eventType | contentId | personId | sessionId | userAgent | userRegion | userCountry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1465413032 | VIEW | -3499919498720038879 | -8845298781299428018 | 1264196770339959068 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1 | 1465412560 | VIEW | 8890720798209849691 | -1032019229384696495 | 3621737643587579081 | Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_11_2... | NY | US |
| 2 | 1465416190 | VIEW | 310515487419366995 | -1130272294246983140 | 2631864456530402479 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 3 | 1465413895 | FOLLOW | 310515487419366995 | 344280948527967603 | -3167637573980064150 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 4 | 1465412290 | VIEW | -7820640624231356730 | -445337111692715325 | 5611481178424124714 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
3. Preprocessing
3.1 Weight
데이터에서 확인하였듯 상호 작용 유형이 다르기 때문에 가중치를 통해 유형별 관심의 정도를 설정한다.
event_type_strength = {
'VIEW': 1.0,
'LIKE': 2.0,
'BOOKMARK': 2.5,
'FOLLOW': 3.0,
'COMMENT CREATED': 4.0,
}
interactions_df['eventStrength'] = interactions_df['eventType'].apply(lambda x: event_type_strength[x])
3.2 Cold-start
추천 시스템은 사용자 cold-start 문제가 있다. 이는 소비한 아이템의 수가 없거나 매우 적은 경우 사용자의 선호도 모델링을 위해 필요한 정보들이 부족하여 개인화된 추천을 제공하기 어려운 경우이다. 따라서 이번 실습에서는 기사와 5개 이상의 상호 작용이 있는 사용자만 추천을 제공하고자 한다.
users_interactions_count_df = interactions_df.groupby(['personId', 'contentId']).size().groupby('personId').size()
print('# 사용자 수: %d' % len(users_interactions_count_df))
users_with_enough_interactions_df = users_interactions_count_df[users_interactions_count_df >= 5].reset_index()[['personId']]
print('# 최소 5번의 상호작용을 한 사용자: %d' % len(users_with_enough_interactions_df))
# 사용자 수: 1895
# 최소 5번의 상호작용을 한 사용자: 1140
print('# 상호작용 수: %d' % len(interactions_df))
interactions_from_selected_users_df = interactions_df.merge(users_with_enough_interactions_df,
how = 'right',
left_on = 'personId',
right_on = 'personId')
print('# 최소 5번의 상호작용을 한 사용자들이 수행한 상호작용 수: %d' % len(interactions_from_selected_users_df))
# 상호작용 수: 72312
# 최소 5번의 상호작용을 한 사용자들이 수행한 상호작용 수: 69868
3.3 Aggregation
사용자는 기사를 여러번 볼 수 있고, 좋아요나 댓글을 다는 상호작용 또한 동시에 수행할 수 있다. 따라서 사용자가 기사에서 행한 모든 상호작용의 가중치를 모두 합하는 집계 작업을 수행한다. 이후 집계된 데이터의 분포를 부드럽게 하기 위해 로그 변환을 적용한다.
# 로그변환 함수
def smooth_user_preference(x):
return math.log(1+x, 2)
interactions_full_df = interactions_from_selected_users_df \
.groupby(['personId', 'contentId'])['eventStrength'].sum() \
.apply(smooth_user_preference).reset_index()
print('# of unique user/item interactions: %d' % len(interactions_full_df))
interactions_full_df.head(10)
# of unique user/item interactions: 39106
| personId | contentId | eventStrength | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -9223121837663643404 | -8949113594875411859 | 1.000000 |
| 1 | -9223121837663643404 | -8377626164558006982 | 1.000000 |
| 2 | -9223121837663643404 | -8208801367848627943 | 1.000000 |
| 3 | -9223121837663643404 | -8187220755213888616 | 1.000000 |
| 4 | -9223121837663643404 | -7423191370472335463 | 3.169925 |
| 5 | -9223121837663643404 | -7331393944609614247 | 1.000000 |
| 6 | -9223121837663643404 | -6872546942144599345 | 1.000000 |
| 7 | -9223121837663643404 | -6728844082024523434 | 1.000000 |
| 8 | -9223121837663643404 | -6590819806697898649 | 1.000000 |
| 9 | -9223121837663643404 | -6558712014192834002 | 1.584963 |
4. Evaluation
4.1 Data split
평가의 키 포인트는 cross-validation을 통해 학습된 모델을 학습되지 않은 데이터에 대해 일반화 시키는 것이다. 이번 실습에서는 데이터의 20%를 test에 사용한 holdout 방식의 cross-validation을 수행한다. 더 정확한 평가를 위해 날짜 기준으로 구분을 해야 하나, 단순성을 위해 랜덤하게 추출하는 방식을 사용한다.
interactions_train_df, interactions_test_df = train_test_split(interactions_full_df,
stratify=interactions_full_df['personId'],
test_size=0.20,
random_state=42)
print('# Train data의 상호작용 수: %d' % len(interactions_train_df))
print('# Test data의 상호작용 수: %d' % len(interactions_test_df))
# Train data의 상호작용 수: 31284
# Test data의 상호작용 수: 7822
4.2 Metric
추천 시스템을 위한 metric은 해당 포스트를 참고하며, 이번 실습에서는 Top-N에 대한 정확도를 평가하는 Recall@N을 사용한다.
4.3 Evaluation
평가는 다음과 같이 수행된다.
- 각 사용자에 대해
- test data에서 사용자가 상호작용한 각 아이템에 대해
- 사용자가 상호작용한 적 없는 100개의 다른 아이템들을 샘플링함
- 위에서 선택한 1개의 상호작용한 아이템과 샘플링한 100개의 상호작용한 적 없는(non-relevant) 아이템을 사용해 추천 순위 리스트를 생성함
- 추천 순위 리스트에서 Top-N에 대한 metric을 수행함
- test data에서 사용자가 상호작용한 각 아이템에 대해
- 모든 metric에 대한 집계 수행
Recall@N은 101개 추천 순위 리스트에서 상호작용한 1개의 아이템이 Top-N에 속하는지 여부를 평가한다.
# 평가 속도를 빠르게 하기 위한 personId 인덱싱 작업
# 각 DataFrame의 인덱스가 personId가 되게 함
interactions_full_indexed_df = interactions_full_df.set_index('personId')
interactions_train_indexed_df = interactions_train_df.set_index('personId')
interactions_test_indexed_df = interactions_test_df.set_index('personId')
def get_items_interacted(person_id, interactions_df):
# 사용가 상호작용한 아이템들을 구함
# set을 쓰는 이유는 향후 집합 연산을 수행하기 때문
interacted_items = interactions_df.loc[person_id]['contentId']
return set(interacted_items if type(interacted_items) == pd.Series else [interacted_items])
# 샘플링할 상호작용 하지 않은 아이템 수
EVAL_RANDOM_SAMPLE_NON_INTERACTED_ITEMS = 100
class ModelEvaluator:
def get_not_interacted_items_sample(self, person_id, sample_size, seed=42):
interacted_items = get_items_interacted(person_id, interactions_full_indexed_df)
all_items = set(articles_df['contentId'])
# 모든 아이템 집합과 상호작용한 아이템 집합의 차집합
non_interacted_items = all_items - interacted_items
random.seed(seed)
# 상호작용하지 않은 아이템에서 sample_size만큼 샘플링
non_interacted_items_sample = random.sample(non_interacted_items, sample_size)
return set(non_interacted_items_sample)
def _verify_hit_top_n(self, item_id, recommended_items, topn):
try:
# item_id가 recommended_items의 몇번째에 위치하고 있는지(index) 구함
index = next(i for i, c in enumerate(recommended_items) if c == item_id)
except:
index = -1
# index가 topn의 범위 안에 속하면 hit(=1) 아니면 not hit(=0)
hit = int(index in range(0, topn))
return hit, index
def evaluate_model_for_user(self, model, person_id):
# test data에서 아이템을 추출
interacted_values_testset = interactions_test_indexed_df.loc[person_id]
if type(interacted_values_testset['contentId']) == pd.Series:
person_interacted_items_testset = set(interacted_values_testset['contentId'])
else:
person_interacted_items_testset = set([int(interacted_values_testset['contentId'])])
# TODO
# person_interacted_items_testset = get_items_interacted(person_id, interactions_test_indexed_df)
interacted_items_count_testset = len(person_interacted_items_testset)
# 모델로 추천 순위 리스트를 생성함
person_recs_df = model.recommend_items(person_id,
items_to_ignore=get_items_interacted(person_id,
interactions_train_indexed_df),
topn=10000000000)
hits_at_5_count = 0
hits_at_10_count = 0
# test data에서 사용자가 상호작용한 각 아이템에 대해
for item_id in person_interacted_items_testset:
# 사용자가 상호작용한 적 없는 100개의 다른 아이템들을 샘플링함
non_interacted_items_sample = self.get_not_interacted_items_sample(person_id,
sample_size=EVAL_RANDOM_SAMPLE_NON_INTERACTED_ITEMS,
seed=item_id%(2**32))
# 위에서 선택한 1개의 상호작용한 아이템과 샘플링한 100개의 상호작용한 적 없는(non-relevant) 아이템을 사용해 추천 순위 리스트를 생성함
items_to_filter_recs = non_interacted_items_sample.union(set([item_id]))
# 모델로 생성한 추천 순위 리스트에서 샘플링을 통한 추천 리스트들을 필터링
valid_recs_df = person_recs_df[person_recs_df['contentId'].isin(items_to_filter_recs)]
valid_recs = valid_recs_df['contentId'].values
# 현재 아이템이 추천 순위 리스트의 상위 N개에 포함되는지 확인
hit_at_5, index_at_5 = self._verify_hit_top_n(item_id, valid_recs, 5)
hits_at_5_count += hit_at_5
hit_at_10, index_at_10 = self._verify_hit_top_n(item_id, valid_recs, 10)
hits_at_10_count += hit_at_10
# 추천 순위 리스트에서 Top-N에 대한 metric을 수행함
recall_at_5 = hits_at_5_count / float(interacted_items_count_testset)
recall_at_10 = hits_at_10_count / float(interacted_items_count_testset)
person_metrics = {'hits@5_count':hits_at_5_count,
'hits@10_count':hits_at_10_count,
'interacted_count': interacted_items_count_testset,
'recall@5': recall_at_5,
'recall@10': recall_at_10}
return person_metrics
def evaluate_model(self, model):
people_metrics = []
for idx, person_id in enumerate(list(interactions_test_indexed_df.index.unique().values)):
person_metrics = self.evaluate_model_for_user(model, person_id)
person_metrics['_person_id'] = person_id
people_metrics.append(person_metrics)
print('%d 명의 사용자 평가 수행' % idx)
detailed_results_df = pd.DataFrame(people_metrics) \
.sort_values('interacted_count', ascending=False)
# 모든 metric에 대한 집계 수행
global_recall_at_5 = detailed_results_df['hits@5_count'].sum() / float(detailed_results_df['interacted_count'].sum())
global_recall_at_10 = detailed_results_df['hits@10_count'].sum() / float(detailed_results_df['interacted_count'].sum())
global_metrics = {'modelName': model.get_model_name(),
'recall@5': global_recall_at_5,
'recall@10': global_recall_at_10}
return global_metrics, detailed_results_df
model_evaluator = ModelEvaluator()
5. Modeling
5.1 Popularity model
Popularity model은 개인화된 추천이 아니라 사용자가 이전에 소비하지 않은 것 중 가장 인기 있는 아이템을 사용자에게 추천할 뿐이다. 이러한 방식은 군중 심리를 포함하고 있기 때문에 때로는 좋은 추천을 제공하기도 한다.
# 사용자 상호작용의 가중합이 높은 순서로 정렬
item_popularity_df = interactions_full_df.groupby('contentId')['eventStrength'].sum().sort_values(ascending=False).reset_index()
item_popularity_df.head(10)
| contentId | eventStrength | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -4029704725707465084 | 307.733799 |
| 1 | -6783772548752091658 | 233.762157 |
| 2 | -133139342397538859 | 228.024567 |
| 3 | -8208801367848627943 | 197.107608 |
| 4 | -6843047699859121724 | 193.825208 |
| 5 | 8224860111193157980 | 189.044680 |
| 6 | -2358756719610361882 | 183.110951 |
| 7 | 2581138407738454418 | 180.282876 |
| 8 | 7507067965574797372 | 179.094002 |
| 9 | 1469580151036142903 | 170.548969 |
class PopularityRecommender:
MODEL_NAME = 'Popularity'
def __init__(self, popularity_df, items_df=None):
self.popularity_df = popularity_df
self.items_df = items_df
def get_model_name(self):
return self.MODEL_NAME
def recommend_items(self, user_id, items_to_ignore=[], topn=10, verbose=False):
# 사용자가 보지 않은 아이템 중 인기도(가중합) 순으로 높은 것을 추천
recommendations_df = self.popularity_df[~self.popularity_df['contentId'].isin(items_to_ignore)] \
.sort_values('eventStrength', ascending = False) \
.head(topn)
if verbose:
if self.items_df is None:
raise Exception('"items_df" is required in verbose mode')
recommendations_df = recommendations_df.merge(self.items_df, how = 'left',
left_on = 'contentId',
right_on = 'contentId')[['eventStrength', 'contentId', 'title', 'url', 'lang']]
return recommendations_df
popularity_model = PopularityRecommender(item_popularity_df, articles_df)
print('Evaluating Popularity recommendation model...')
pop_global_metrics, pop_detailed_results_df = model_evaluator.evaluate_model(popularity_model)
print('\nGlobal metrics:\n%s' % pop_global_metrics)
pop_detailed_results_df.head(10)
Evaluating Popularity recommendation model...
1139 명의 사용자 평가 수행
Global metrics:
{'modelName': 'Popularity', 'recall@5': 0.2418818716440808, 'recall@10': 0.3725389925850166}
| hits@5_count | hits@10_count | interacted_count | recall@5 | recall@10 | _person_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 28 | 50 | 192 | 0.145833 | 0.260417 | 3609194402293569455 |
| 17 | 12 | 25 | 134 | 0.089552 | 0.186567 | -2626634673110551643 |
| 16 | 13 | 23 | 130 | 0.100000 | 0.176923 | -1032019229384696495 |
| 10 | 5 | 9 | 117 | 0.042735 | 0.076923 | -1443636648652872475 |
| 82 | 26 | 40 | 88 | 0.295455 | 0.454545 | -2979881261169775358 |
| 161 | 12 | 18 | 80 | 0.150000 | 0.225000 | -3596626804281480007 |
| 65 | 20 | 34 | 73 | 0.273973 | 0.465753 | 1116121227607581999 |
| 81 | 17 | 23 | 69 | 0.246377 | 0.333333 | 692689608292948411 |
| 106 | 14 | 18 | 69 | 0.202899 | 0.260870 | -9016528795238256703 |
| 52 | 21 | 28 | 68 | 0.308824 | 0.411765 | 3636910968448833585 |
5.2 Content-Based Filtering model
Content-based filtering 방식은 사용자가 상호 작용한 아이템의 profile을 활용하여 유사한 아이템을 추천한다. (단, 이는 사용자의 이전 선택에만 의존하므로 cold-start 문제 방지를 위한 기법들이 필요하다.) 기사, 뉴스 및 책과 같은 텍스트 항목의 경우 자연어 처리 기법을 사용하여 아이템 및 사용자의 profile을 정의할 수 있다. 이번 실습에서는 자연어 처리의 기법 중 하나인 TF-IDF를 사용한다. 이는 간단히 말해 보유한 데이터를 모든 문서 대 모든 단어의 matrix를 만들어 각 단어가 문서에서 얼마나 관련이 있는지를 나타내는 것이다.
# 영어, 포르투칼어의 불용어를 제거함
stopwords_list = stopwords.words('english') + stopwords.words('portuguese')
# TfidfVectorizer 모델 생성
vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(analyzer='word',
ngram_range=(1, 2), # unigram or bigram
min_df=0.003,
max_df=0.5,
max_features=5000,
stop_words=stopwords_list)
# 기사 리스트 생성
item_ids = articles_df['contentId'].tolist()
# 현재 기사들에 대해 TfidfVectorizer 모델 학습
tfidf_matrix = vectorizer.fit_transform(articles_df['title'] + "" + articles_df['text'])
# unigram or bigram의 토큰 리스트 생성
tfidf_feature_names = vectorizer.get_feature_names()
tfidf_matrix
<3047x5000 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.float64'>'
with 638118 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format>
사용자 profile은 사용자가 상호 작용한 모든 아이템들의 profile들의 평균을 통해 구한다. 이 때, 각 상호작용의 강도에 따라 가중치를 부여하여 평균을 구한다.
def get_item_profile(item_id):
idx = item_ids.index(item_id)
item_profile = tfidf_matrix[idx:idx+1]
return item_profile
def get_item_profiles(ids):
item_profiles_list = [get_item_profile(x) for x in ids]
item_profiles = scipy.sparse.vstack(item_profiles_list)
return item_profiles
def build_users_profile(person_id, interactions_indexed_df):
interactions_person_df = interactions_indexed_df.loc[person_id]
user_item_profiles = get_item_profiles(interactions_person_df['contentId'])
user_item_strengths = np.array(interactions_person_df['eventStrength']).reshape(-1,1)
# 가중치를 적용한 상호작용 강도의 평균을 구한 뒤 normalize를 진행한다 (단위 벡터로 만들어주기 위함)
user_item_strengths_weighted_avg = np.sum(user_item_profiles.multiply(user_item_strengths), axis=0) / np.sum(user_item_strengths)
user_profile_norm = sklearn.preprocessing.normalize(user_item_strengths_weighted_avg)
return user_profile_norm
def build_users_profiles():
interactions_indexed_df = interactions_train_df[interactions_train_df['contentId'] \
.isin(articles_df['contentId'])].set_index('personId')
user_profiles = {}
for person_id in interactions_indexed_df.index.unique():
user_profiles[person_id] = build_users_profile(person_id, interactions_indexed_df)
return user_profiles
user_profiles = build_users_profiles()
len(user_profiles)
1140
profile은 길이가 5000인 단위 벡터이며, 각 위치의 값은 토큰(unigram 혹은 bigram)이 나에게 얼마나 관련있는지를 나타낸다. 아래 예시를 보면 사용자가 관심있는 내용이 유사한 형태로 나타남을 볼 수 있다.
myprofile = user_profiles[-1479311724257856983]
print(myprofile.shape)
pd.DataFrame(sorted(zip(tfidf_feature_names,
user_profiles[-1479311724257856983].flatten().tolist()), key=lambda x: -x[1])[:20],
columns=['token', 'relevance'])
(1, 5000)
| token | relevance | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | learning | 0.298835 |
| 1 | machine learning | 0.246087 |
| 2 | machine | 0.237933 |
| 3 | 0.203117 | |
| 4 | data | 0.169849 |
| 5 | ai | 0.156280 |
| 6 | algorithms | 0.115706 |
| 7 | like | 0.097790 |
| 8 | language | 0.087673 |
| 9 | people | 0.082061 |
| 10 | deep | 0.081565 |
| 11 | deep learning | 0.081005 |
| 12 | research | 0.076052 |
| 13 | algorithm | 0.074934 |
| 14 | apple | 0.074144 |
| 15 | intelligence | 0.072694 |
| 16 | use | 0.072631 |
| 17 | human | 0.072517 |
| 18 | models | 0.072435 |
| 19 | artificial | 0.072179 |
class ContentBasedRecommender:
MODEL_NAME = 'Content-Based'
def __init__(self, items_df=None):
self.item_ids = item_ids
self.items_df = items_df
def get_model_name(self):
return self.MODEL_NAME
def _get_similar_items_to_user_profile(self, person_id, topn=1000):
# 모든 아이템 profile들과 사용자 profile의 cosine 유사도를 계산함
cosine_similarities = cosine_similarity(user_profiles[person_id], tfidf_matrix)
# 가장 유사한 topn의 아이템 선정
similar_indices = cosine_similarities.argsort().flatten()[-topn:]
similar_items = sorted([(item_ids[i], cosine_similarities[0,i]) for i in similar_indices], key=lambda x: -x[1])
return similar_items
def recommend_items(self, user_id, items_to_ignore=[], topn=10, verbose=False):
similar_items = self._get_similar_items_to_user_profile(user_id)
similar_items_filtered = list(filter(lambda x: x[0] not in items_to_ignore, similar_items))
recommendations_df = pd.DataFrame(similar_items_filtered, columns=['contentId', 'recStrength']) \
.head(topn)
if verbose:
if self.items_df is None:
raise Exception('"items_df" is required in verbose mode')
recommendations_df = recommendations_df.merge(self.items_df, how = 'left',
left_on = 'contentId',
right_on = 'contentId')[['recStrength', 'contentId', 'title', 'url', 'lang']]
return recommendations_df
content_based_recommender_model = ContentBasedRecommender(articles_df)
print('Evaluating Content-Based Filtering model...')
cb_global_metrics, cb_detailed_results_df = model_evaluator.evaluate_model(content_based_recommender_model)
print('\nGlobal metrics:\n%s' % cb_global_metrics)
cb_detailed_results_df.head(10)
Evaluating Content-Based Filtering model...
1139 명의 사용자 평가 수행
Global metrics:
{'modelName': 'Content-Based', 'recall@5': 0.16338532344668882, 'recall@10': 0.26118639734083354}
| hits@5_count | hits@10_count | interacted_count | recall@5 | recall@10 | _person_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 15 | 24 | 192 | 0.078125 | 0.125000 | 3609194402293569455 |
| 17 | 18 | 29 | 134 | 0.134328 | 0.216418 | -2626634673110551643 |
| 16 | 20 | 33 | 130 | 0.153846 | 0.253846 | -1032019229384696495 |
| 10 | 32 | 46 | 117 | 0.273504 | 0.393162 | -1443636648652872475 |
| 82 | 6 | 15 | 88 | 0.068182 | 0.170455 | -2979881261169775358 |
| 161 | 11 | 23 | 80 | 0.137500 | 0.287500 | -3596626804281480007 |
| 65 | 8 | 13 | 73 | 0.109589 | 0.178082 | 1116121227607581999 |
| 81 | 8 | 19 | 69 | 0.115942 | 0.275362 | 692689608292948411 |
| 106 | 3 | 9 | 69 | 0.043478 | 0.130435 | -9016528795238256703 |
| 52 | 3 | 8 | 68 | 0.044118 | 0.117647 | 3636910968448833585 |
5.3 Collaborative Filtering model
Collaborative Filtering (CF)은 아래와 같은 두 가지 구현 방식이 있다.
-
Memory-based
이 방법은 사용자가 상호 작용한 아이템을 기반으로 사용자 유사성을 계산하거나 사용자와 상호 작용한 사용자를 기반으로 아이템 유사성을 계산한다. 대표적인 예로는 User Neighbourhood-based CF로, 사용자에 대한 top-N의 유사한 사용자(일반적으로 Pearson 상관관계를 사용하여 계산)를 선택하여 유사한 사용자가 좋아하는 아이템을 추천하는 데 사용된다. 이는 구현하기 간단하지만 일반적으로 많은 사용자가 많아질 경우 확장하기 어렵다는 단점이 있다. -
Model-based ★★
다양한 기계 학습 알고리즘을 사용하여 사용자에게 아이템을 추천하는 모델을 개발한다. neural network, bayesian network, clustering model과 같은 모델 기반 CF 알고리즘과 Singular Value Decomposition(SVD) 및 probabilistic latent semantic analysis와 같은 latent factor model이 있다.
5.4 Matrix Factorization(MF)
Latent factor model을 사용하는 MF는 user-item matrix를 저차원의 표현(latent factor)으로 압축한다. 이러한 방식은 많은 결측값을 포함하는 고차원 matrix가 아닌 저차원의 작은 matrix를 다루기 때문에 memory-based에서 사용하는 matrix 보다 희소성 문제를 잘 처리한다는 장점이 있다. 또한 축소된 matrix를 통해 유사도 비교를 하기 떄문에 확장성이 좋아 대규모의 희소 데이터 세트를 다룸에 있어 강점이 있다. 이번 실습에서는 다양한 Latent factor model 중 SVD를 사용한다. Movie dataset SVD 적용에 대한 예시는 이 글을 참조한다.
SVD를 수행함에 있어 중요한 것은 user-item matrix의 factor(차원)의 수를 결정하는 것이다. factor가 많아질 수록 matrix를 분해한 결과가 원본에 가까워질 것이다. 이러한 경우 모델이 학습하지 않은 데이터들에 대해 일반화시키지 못하는 과적합 현상이 발생할 수 있다. 따라서 요인의 개수를 적절히 줄이는 것이 모델의 일반화에 도움이 될 수 있다.
# pivot을 통해 사용자 대 아이템(user-item) matrix를 만들고 빈값(사용자가 상호작용하지 않은 아이템)은 0으로 채운다
users_items_pivot_matrix_df = interactions_train_df.pivot(index='personId',
columns='contentId',
values='eventStrength').fillna(0)
users_items_pivot_matrix_df.head(10)
| contentId | -9222795471790223670 | -9216926795620865886 | -9194572880052200111 | -9192549002213406534 | -9190737901804729417 | -9189659052158407108 | -9176143510534135851 | -9172673334835262304 | -9171475473795142532 | -9166778629773133902 | ... | 9191014301634017491 | 9207286802575546269 | 9208127165664287660 | 9209629151177723638 | 9209886322932807692 | 9213260650272029784 | 9215261273565326920 | 9217155070834564627 | 9220445660318725468 | 9222265156747237864 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| personId | |||||||||||||||||||||
| -9223121837663643404 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9212075797126931087 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9207251133131336884 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9199575329909162940 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9196668942822132778 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9188188261933657343 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9172914609055320039 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9156344805277471150 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9120685872592674274 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| -9109785559521267180 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
10 rows × 2926 columns
users_items_pivot_matrix = users_items_pivot_matrix_df.values
users_items_pivot_matrix[:2]
array([[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.]])
users_ids = list(users_items_pivot_matrix_df.index)
users_ids[:10]
[-9223121837663643404,
-9212075797126931087,
-9207251133131336884,
-9199575329909162940,
-9196668942822132778,
-9188188261933657343,
-9172914609055320039,
-9156344805277471150,
-9120685872592674274,
-9109785559521267180]
만들어진 사용자 대 아이템 matrix는 대부분이 0으로 된 sparse한 matrix이다. 이는 계산시 불필요한 메모리가 많이 소요되기 때문에 CSR 또는 COO 변환이 필요하다. 이러한 기법에 대한 내용은 COO와 CSR를 통해 확인하며, 이번 실습에서는 CSR 방식을 사용한다.
users_items_pivot_sparse_matrix = csr_matrix(users_items_pivot_matrix)
users_items_pivot_sparse_matrix
<1140x2926 sparse matrix of type '<class 'numpy.float64'>'
with 31284 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format>
# user-item matrix의 factor를 정함
NUMBER_OF_FACTORS_MF = 15
# user-item matrix를 SVD를 사용해 분해
U, sigma, Vt = svds(users_items_pivot_sparse_matrix, k = NUMBER_OF_FACTORS_MF)
U.shape
(1140, 15)
Vt.shape
(15, 2926)
sigma = np.diag(sigma)
sigma.shape
(15, 15)
분해된 matrix의 요소 U, sigma, Vt를 다시 곱하여 원래의 matrix의 크기로 복원한 결과는 더이상 sparse 하지 않게 된다. 이는 사용자가 상호작용 하지 않은 아이템에 대한 예측을 생성한 것과 같으며 이를 추천하는 아이템으로 활용한다.
all_user_predicted_ratings = np.dot(np.dot(U, sigma), Vt)
all_user_predicted_ratings
array([[ 0.01039915, 0.00081872, -0.01725263, ..., 0.00140708,
0.0110647 , 0.00226063],
[-0.00019285, -0.00031318, -0.00264624, ..., 0.00251658,
0.00017609, -0.00189488],
[-0.01254721, 0.0065947 , -0.00590676, ..., 0.00698975,
-0.01015696, 0.01154572],
...,
[-0.02995379, 0.00805715, -0.01846307, ..., -0.01083078,
-0.00118591, 0.0096798 ],
[-0.01845505, 0.00467019, 0.01219602, ..., 0.00409507,
0.00019482, -0.00752562],
[-0.01506374, 0.00327732, 0.13391269, ..., -0.01191815,
0.06422074, 0.01303244]])
print("행:", len(all_user_predicted_ratings))
print("열:", len(all_user_predicted_ratings[0]))
행: 1140
열: 2926
# matrix 정규화
all_user_predicted_ratings_norm = (all_user_predicted_ratings - all_user_predicted_ratings.min()) / \
(all_user_predicted_ratings.max() - all_user_predicted_ratings.min())
# Dataframe(item-user matrix)으로 변환
cf_preds_df = pd.DataFrame(all_user_predicted_ratings_norm, columns = users_items_pivot_matrix_df.columns, index=users_ids).transpose()
cf_preds_df.head(10)
| -9223121837663643404 | -9212075797126931087 | -9207251133131336884 | -9199575329909162940 | -9196668942822132778 | -9188188261933657343 | -9172914609055320039 | -9156344805277471150 | -9120685872592674274 | -9109785559521267180 | ... | 9105269044962898535 | 9109075639526981934 | 9135582630122950040 | 9137372837662939523 | 9148269800512008413 | 9165571805999894845 | 9187866633451383747 | 9191849144618614467 | 9199170757466086545 | 9210530975708218054 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| contentId | |||||||||||||||||||||
| -9222795471790223670 | 0.139129 | 0.137930 | 0.136531 | 0.143948 | 0.136815 | 0.137339 | 0.137508 | 0.143534 | 0.136428 | 0.135681 | ... | 0.137351 | 0.127822 | 0.137946 | 0.139653 | 0.140324 | 0.136888 | 0.135787 | 0.134560 | 0.135862 | 0.136246 |
| -9216926795620865886 | 0.138044 | 0.137916 | 0.138698 | 0.137878 | 0.137969 | 0.137990 | 0.137974 | 0.138049 | 0.138217 | 0.138151 | ... | 0.137962 | 0.139527 | 0.138009 | 0.138117 | 0.139634 | 0.138058 | 0.138222 | 0.138864 | 0.138480 | 0.138323 |
| -9194572880052200111 | 0.135998 | 0.137652 | 0.137283 | 0.137536 | 0.140363 | 0.137807 | 0.141246 | 0.136284 | 0.135301 | 0.138512 | ... | 0.139257 | 0.143161 | 0.139139 | 0.140077 | 0.154976 | 0.140109 | 0.140654 | 0.135861 | 0.139332 | 0.153114 |
| -9192549002213406534 | 0.141924 | 0.137996 | 0.134663 | 0.137080 | 0.139946 | 0.138574 | 0.139473 | 0.144469 | 0.143333 | 0.138428 | ... | 0.140233 | 0.167426 | 0.138849 | 0.137037 | 0.141820 | 0.139260 | 0.139513 | 0.136804 | 0.140862 | 0.148793 |
| -9190737901804729417 | 0.140209 | 0.137408 | 0.138708 | 0.138672 | 0.137725 | 0.138218 | 0.138390 | 0.138418 | 0.134883 | 0.140193 | ... | 0.138373 | 0.138459 | 0.138169 | 0.137990 | 0.134041 | 0.137820 | 0.138100 | 0.138286 | 0.138630 | 0.136178 |
| -9189659052158407108 | 0.138932 | 0.138699 | 0.138117 | 0.137621 | 0.138920 | 0.137766 | 0.138568 | 0.138200 | 0.140572 | 0.140365 | ... | 0.140725 | 0.148152 | 0.137645 | 0.138165 | 0.149152 | 0.138912 | 0.139595 | 0.139807 | 0.140419 | 0.145698 |
| -9176143510534135851 | 0.143208 | 0.138673 | 0.139514 | 0.139114 | 0.137664 | 0.137447 | 0.139833 | 0.140564 | 0.144698 | 0.144440 | ... | 0.138367 | 0.146220 | 0.136204 | 0.138087 | 0.137317 | 0.137917 | 0.138546 | 0.142601 | 0.141431 | 0.142154 |
| -9172673334835262304 | 0.138527 | 0.138021 | 0.138274 | 0.137827 | 0.137997 | 0.138037 | 0.138104 | 0.138259 | 0.137633 | 0.138397 | ... | 0.138588 | 0.140146 | 0.138013 | 0.137839 | 0.137033 | 0.137969 | 0.138337 | 0.138361 | 0.138813 | 0.137538 |
| -9171475473795142532 | 0.140720 | 0.137865 | 0.138061 | 0.137633 | 0.138231 | 0.138089 | 0.139009 | 0.137552 | 0.137143 | 0.140581 | ... | 0.139046 | 0.139895 | 0.138000 | 0.137958 | 0.136061 | 0.138183 | 0.138817 | 0.138060 | 0.139205 | 0.137198 |
| -9166778629773133902 | 0.138989 | 0.137725 | 0.136520 | 0.137723 | 0.138559 | 0.137951 | 0.138189 | 0.138496 | 0.139470 | 0.137546 | ... | 0.138233 | 0.144002 | 0.138050 | 0.137533 | 0.139036 | 0.138399 | 0.138330 | 0.137148 | 0.138027 | 0.140283 |
10 rows × 1140 columns
class CFRecommender:
MODEL_NAME = 'Collaborative Filtering'
def __init__(self, cf_predictions_df, items_df=None):
self.cf_predictions_df = cf_predictions_df
self.items_df = items_df
def get_model_name(self):
return self.MODEL_NAME
def recommend_items(self, user_id, items_to_ignore=[], topn=10, verbose=False):
sorted_user_predictions = self.cf_predictions_df[user_id].sort_values(ascending=False) \
.reset_index().rename(columns={user_id: 'recStrength'})
recommendations_df = sorted_user_predictions[~sorted_user_predictions['contentId'].isin(items_to_ignore)] \
.sort_values('recStrength', ascending = False) \
.head(topn)
if verbose:
if self.items_df is None:
raise Exception('"items_df" is required in verbose mode')
recommendations_df = recommendations_df.merge(self.items_df, how = 'left',
left_on = 'contentId',
right_on = 'contentId')[['recStrength', 'contentId', 'title', 'url', 'lang']]
return recommendations_df
cf_recommender_model = CFRecommender(cf_preds_df, articles_df)
print('Evaluating Collaborative Filtering (SVD Matrix Factorization) model...')
cf_global_metrics, cf_detailed_results_df = model_evaluator.evaluate_model(cf_recommender_model)
print('\nGlobal metrics:\n%s' % cf_global_metrics)
cf_detailed_results_df.head(10)
Evaluating Collaborative Filtering (SVD Matrix Factorization) model...
1139 명의 사용자 평가 수행
Global metrics:
{'modelName': 'Collaborative Filtering', 'recall@5': 0.33392994119151115, 'recall@10': 0.46803886474047557}
| hits@5_count | hits@10_count | interacted_count | recall@5 | recall@10 | _person_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 21 | 46 | 192 | 0.109375 | 0.239583 | 3609194402293569455 |
| 17 | 30 | 56 | 134 | 0.223881 | 0.417910 | -2626634673110551643 |
| 16 | 16 | 34 | 130 | 0.123077 | 0.261538 | -1032019229384696495 |
| 10 | 38 | 51 | 117 | 0.324786 | 0.435897 | -1443636648652872475 |
| 82 | 39 | 48 | 88 | 0.443182 | 0.545455 | -2979881261169775358 |
| 161 | 22 | 34 | 80 | 0.275000 | 0.425000 | -3596626804281480007 |
| 65 | 24 | 32 | 73 | 0.328767 | 0.438356 | 1116121227607581999 |
| 81 | 16 | 21 | 69 | 0.231884 | 0.304348 | 692689608292948411 |
| 106 | 20 | 28 | 69 | 0.289855 | 0.405797 | -9016528795238256703 |
| 52 | 23 | 30 | 68 | 0.338235 | 0.441176 | 3636910968448833585 |
5.5 Hybrid Recommender
Collaborative Filtering과 Content-Based Filtering을 결합한 Hybrid Recommender는 개별 방식들보다 우수한 성능을 보임을 증명하였고, 다양한 실무 영역에서 사용하고 있다. 이번 실습에서 앙상블에 대한 구현은 각 모델의 추천결과에 각 가중치를 곱해 평균을 내는 단순한 방식을 사용한다. 이때 CF 모델이 CB 모델보다 정확하므로 각각의 가중치는 100과 1로 설정하였다.
class HybridRecommender:
MODEL_NAME = 'Hybrid'
def __init__(self, cb_rec_model, cf_rec_model, items_df, cb_ensemble_weight=1.0, cf_ensemble_weight=1.0):
self.cb_rec_model = cb_rec_model
self.cf_rec_model = cf_rec_model
self.cb_ensemble_weight = cb_ensemble_weight
self.cf_ensemble_weight = cf_ensemble_weight
self.items_df = items_df
def get_model_name(self):
return self.MODEL_NAME
def recommend_items(self, user_id, items_to_ignore=[], topn=10, verbose=False):
# top-1000 Content-based filtering 추천 리스트
cb_recs_df = self.cb_rec_model.recommend_items(user_id, items_to_ignore=items_to_ignore, verbose=verbose,
topn=1000).rename(columns={'recStrength': 'recStrengthCB'})
# top-1000 Collaborative filtering 추천 리스트
cf_recs_df = self.cf_rec_model.recommend_items(user_id, items_to_ignore=items_to_ignore, verbose=verbose,
topn=1000).rename(columns={'recStrength': 'recStrengthCF'})
# 두 추천 리스트 병합
recs_df = cb_recs_df.merge(cf_recs_df,
how = 'outer',
left_on = 'contentId',
right_on = 'contentId').fillna(0.0)
# 앙상블 적용
recs_df['recStrengthHybrid'] = (recs_df['recStrengthCB'] * self.cb_ensemble_weight) \
+ (recs_df['recStrengthCF'] * self.cf_ensemble_weight)
recommendations_df = recs_df.sort_values('recStrengthHybrid', ascending=False).head(topn)
if verbose:
if self.items_df is None:
raise Exception('"items_df" is required in verbose mode')
recommendations_df = recommendations_df.merge(self.items_df, how = 'left',
left_on = 'contentId',
right_on = 'contentId')[['recStrengthHybrid', 'contentId', 'title', 'url', 'lang']]
return recommendations_df
hybrid_recommender_model = HybridRecommender(content_based_recommender_model, cf_recommender_model, articles_df,
cb_ensemble_weight=1.0, cf_ensemble_weight=100.0)
print('Evaluating Hybrid model...')
hybrid_global_metrics, hybrid_detailed_results_df = model_evaluator.evaluate_model(hybrid_recommender_model)
print('\nGlobal metrics:\n%s' % hybrid_global_metrics)
hybrid_detailed_results_df.head(10)
Evaluating Hybrid model...
1139 명의 사용자 평가 수행
Global metrics:
{'modelName': 'Hybrid', 'recall@5': 0.3430069036052161, 'recall@10': 0.479033495269752}
| hits@5_count | hits@10_count | interacted_count | recall@5 | recall@10 | _person_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 | 22 | 45 | 192 | 0.114583 | 0.234375 | 3609194402293569455 |
| 17 | 31 | 58 | 134 | 0.231343 | 0.432836 | -2626634673110551643 |
| 16 | 21 | 37 | 130 | 0.161538 | 0.284615 | -1032019229384696495 |
| 10 | 40 | 51 | 117 | 0.341880 | 0.435897 | -1443636648652872475 |
| 82 | 38 | 50 | 88 | 0.431818 | 0.568182 | -2979881261169775358 |
| 161 | 23 | 35 | 80 | 0.287500 | 0.437500 | -3596626804281480007 |
| 65 | 23 | 32 | 73 | 0.315068 | 0.438356 | 1116121227607581999 |
| 81 | 16 | 21 | 69 | 0.231884 | 0.304348 | 692689608292948411 |
| 106 | 20 | 27 | 69 | 0.289855 | 0.391304 | -9016528795238256703 |
| 52 | 22 | 29 | 68 | 0.323529 | 0.426471 | 3636910968448833585 |
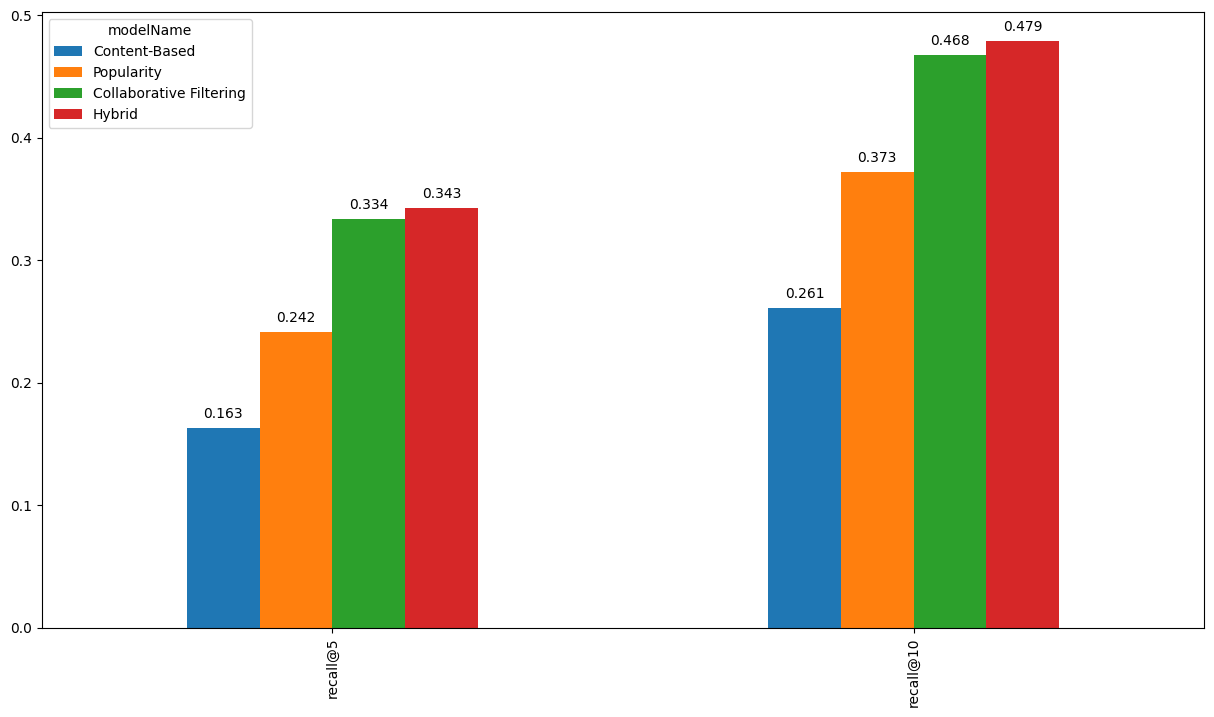
6. Compare result
global_metrics_df = pd.DataFrame([cb_global_metrics, pop_global_metrics, cf_global_metrics, hybrid_global_metrics]) \
.set_index('modelName')
global_metrics_df
| recall@5 | recall@10 | |
|---|---|---|
| modelName | ||
| Content-Based | 0.163385 | 0.261186 |
| Popularity | 0.241882 | 0.372539 |
| Collaborative Filtering | 0.333930 | 0.468039 |
| Hybrid | 0.343007 | 0.479033 |
%matplotlib inline
ax = global_metrics_df.transpose().plot(kind='bar', figsize=(15,8))
for p in ax.patches:
ax.annotate("%.3f" % p.get_height(), (p.get_x() + p.get_width() / 2., p.get_height()), ha='center', va='center', xytext=(0, 10), textcoords='offset points')
7. Test
def inspect_interactions(person_id, test_set=True):
if test_set:
interactions_df = interactions_test_indexed_df
else:
interactions_df = interactions_train_indexed_df
return interactions_df.loc[person_id].merge(articles_df, how = 'left',
left_on = 'contentId',
right_on = 'contentId') \
.sort_values('eventStrength', ascending = False)[['eventStrength',
'contentId',
'title', 'url', 'lang']]
inspect_interactions(-1479311724257856983, test_set=True)
| eventStrength | contentId | title | url | lang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 3.459432 | -532999578436827210 | IBM Seeks to Simplify Graph with New Titan Ser... | https://www.datanami.com/2016/07/27/ibm-seeks-... | en |
| 6 | 3.459432 | -5658245291907121574 | Machine Learning and the VP Debate | https://medium.com/@srobtweets/machine-learnin... | en |
| 9 | 3.000000 | -9033211547111606164 | Google's Cloud Machine Learning service is now... | https://techcrunch.com/2016/09/29/googles-clou... | en |
| 17 | 2.584963 | 524776334673868069 | Graph-powered Machine Learning at Google | https://research.googleblog.com/2016/10/graph-... | en |
| 23 | 2.321928 | -4127059794203205931 | TPOT: A Python tool for automating data science | http://www.randalolson.com/2016/05/08/tpot-a-p... | en |
| 14 | 2.000000 | -3040610224044779845 | Things you probably didn't know you could do w... | https://medium.freecodecamp.com/10-tips-to-max... | en |
| 11 | 2.000000 | -7277691357631151609 | Giant-Man Goes Down in CAPTAIN AMERICA: CIVIL ... | http://geektyrant.com/news/giant-man-goes-down... | en |
| 19 | 2.000000 | -1452340812018195881 | Globo G1 lança Bot para o Telegram que te ajud... | http://www.diolinux.com.br/2016/10/globo-g1-la... | pt |
| 3 | 2.000000 | -7033990154815318757 | The Conversational Economy Part 1: What's Caus... | http://venturebeat.com/2016/06/13/the-conversa... | en |
| 2 | 2.000000 | -3348652277274905234 | Google usa aprendizado de máquina para melhora... | https://googlediscovery.com/2016/11/17/google-... | pt |
| 7 | 1.584963 | 1649085803937938638 | Lilly Wachowski Makes First Public Appearance ... | http://www.usmagazine.com/celebrity-news/news/... | en |
| 4 | 1.584963 | 1179017557429431126 | Imagine Discovering That Your Teaching Assista... | http://www.wsj.com/articles/if-your-teacher-so... | en |
| 16 | 1.584963 | -2065362330475275026 | Minha passagem no Hackathon da Globo #bbb2017 | https://medium.com/@rodrigogd/minha-passagem-n... | pt |
| 26 | 1.584963 | -7550906488404754851 | Governo busca empresas para aprimorar Internet... | http://www.tecmundo.com.br/internet-das-coisas... | pt |
| 27 | 1.000000 | 6016376495317032228 | Uma recepção eficiente | http://vocerh.uol.com.br/noticias/acervo/uma-r... | pt |
| 20 | 1.000000 | -2118981143119783447 | What readers think about computer-generated texts | http://www.en.uni-muenchen.de/news/newsarchiv/... | en |
| 25 | 1.000000 | -1537223691132357350 | A arte de encantar clientes: 5 lições que apre... | https://endeavor.org.br/jeito-disney-encantar-... | pt |
| 24 | 1.000000 | -8909927294729358771 | Android N Developer Preview 2, out today! | An... | http://android-developers.blogspot.com.br/2016... | en |
| 22 | 1.000000 | -8123434787655959885 | Machine learning is a poor fit for most busine... | http://www.infoworld.com/article/3053505/cloud... | en |
| 21 | 1.000000 | 4296604388230897073 | No "Altas Horas", garoto filho de casal homoaf... | https://catracalivre.com.br/geral/cidadania/in... | pt |
| 0 | 1.000000 | 7572869304086387835 | The White House Has Realized Artificial Intell... | http://www.popsci.com/white-house-has-realized... | en |
| 18 | 1.000000 | -6009377241272750648 | Nespresso | https://www.nespresso.com/br/pt/pages/cafeteir... | pt |
| 15 | 1.000000 | -7585525446062170144 | Google launches Duo video calling app, a dull ... | https://techcrunch.com/2016/08/15/google-duo/ | en |
| 1 | 1.000000 | 3472032465864014134 | Pabllo Vittar reina no novo comercial da Skol ... | http://www.superpride.com.br/2016/08/pabllo-vi... | pt |
| 13 | 1.000000 | -23817016428727099 | Being a Developer After 40 | https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=11569726 | en |
| 12 | 1.000000 | 6412479507689487223 | Microsoft's new online certification program k... | http://www.zdnet.com/article/microsofts-new-on... | en |
| 10 | 1.000000 | -4414039190127558142 | BEHOLD Amazon One - the first cargo airplane w... | http://www.businessinsider.com/amazon-one-carg... | en |
| 8 | 1.000000 | 8637400873589298078 | Google launches distributed version of its Ten... | http://techcrunch.com/2016/04/13/google-launch... | en |
| 28 | 1.000000 | 5350829677696205474 | 2016 will be the year of conversational commer... | https://medium.com/chris-messina/2016-will-be-... | en |
hybrid_recommender_model.recommend_items(-1479311724257856983, topn=5, verbose=True)
| recStrengthHybrid | contentId | title | url | lang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25.437103 | 3269302169678465882 | The barbell effect of machine learning. | http://techcrunch.com/2016/06/02/the-barbell-e... | en |
| 1 | 25.369932 | -8085935119790093311 | Graph Capabilities with the Elastic Stack | https://www.elastic.co/webinars/sneak-peek-of-... | en |
| 2 | 24.493428 | 1005751836898964351 | Seria Stranger Things uma obra de arte do algo... | https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/seria-stranger-... | pt |
| 3 | 24.383245 | -8377626164558006982 | Bad Writing Is Destroying Your Company's Produ... | https://hbr.org/2016/09/bad-writing-is-destroy... | en |
| 4 | 24.362064 | -6727357771678896471 | This Super Accurate Portrait Selection Tech Us... | http://petapixel.com/2016/06/29/super-accurate... | en |
test_user = inspect_interactions(-1479311724257856983, test_set=True)
test_rec = hybrid_recommender_model.recommend_items(-1479311724257856983, topn=30, verbose=True)
댓글남기기